 The world of microorganisms and sample identification is truly fascinating, but only if you are using the correct equipment. Today, we will be focusing on the polarized light microscope (PLM). The team at SanAir Technologies Laboratory has put together this article to help you understand what polarized light microscopes are, as well as how they can be used for sample identification.
The world of microorganisms and sample identification is truly fascinating, but only if you are using the correct equipment. Today, we will be focusing on the polarized light microscope (PLM). The team at SanAir Technologies Laboratory has put together this article to help you understand what polarized light microscopes are, as well as how they can be used for sample identification.
Polarized light microscopes direct a beam of altered light, called polarized light, through a sample. The beam travels through a series of filters that change the polarity and wavelength of the light, and the result is a very high-contrast image. PLM analysis is regularly used for analyzing bones, teeth, muscles, geological features, and asbestos.





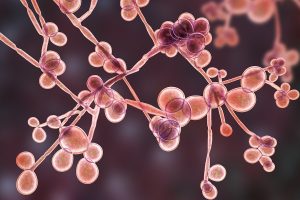 When it comes to sample testing, our lab can test for specific substances like asbestos or lead, but to test for the presence of living organisms, we can opt to use microbiology identification. In the microbiology identification process, scientists examine samples in a variety of ways and run a series of tests to draw conclusions about the presence of microorganisms in the sample. In homes and businesses, this can be particularly helpful in testing air samples for the presence of mold and microorganisms.
When it comes to sample testing, our lab can test for specific substances like asbestos or lead, but to test for the presence of living organisms, we can opt to use microbiology identification. In the microbiology identification process, scientists examine samples in a variety of ways and run a series of tests to draw conclusions about the presence of microorganisms in the sample. In homes and businesses, this can be particularly helpful in testing air samples for the presence of mold and microorganisms.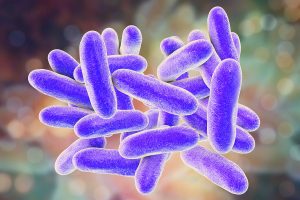 In the fall of 2017, an outbreak of harmful bacteria linked to the cooling mist at Disneyland in California caused 22 people to develop Legionnaires’ disease, resulting in one fatality. In
In the fall of 2017, an outbreak of harmful bacteria linked to the cooling mist at Disneyland in California caused 22 people to develop Legionnaires’ disease, resulting in one fatality. In  When we think of combustion engines and the pollutants they produce, we typically picture cars and trucks driving along the interstate. In fact, we rarely think that there would be contamination from these combustion processes inside of our homes and businesses. If you’ve ever noticed a black stain on your carpet, around your wall outlets, or near ventilation grates, you may have a carbon black or soot problem on your hands. Carbon black and soot can both pose a significant risk to the health of you and your family if left undetected and untreated.
When we think of combustion engines and the pollutants they produce, we typically picture cars and trucks driving along the interstate. In fact, we rarely think that there would be contamination from these combustion processes inside of our homes and businesses. If you’ve ever noticed a black stain on your carpet, around your wall outlets, or near ventilation grates, you may have a carbon black or soot problem on your hands. Carbon black and soot can both pose a significant risk to the health of you and your family if left undetected and untreated.







